Inflammation and The Ayurvedic Remedy
What would anyone give for ageless skin? Skin soft and radiant as a rose, smooth as butter, and supple. One would give, dare we say, their right arm!
Did you know the skin is the largest organ in the human body? It is also the first line of defense against any onslaughts that can cause harm to the body. It can absorb whatever you put on it as it is porous. Therefore, it is critical to be aware of what you put topically on your skin. Ayurveda, a five-thousand-year-old medicinal science from India, goes a step further and says what you eat is also vital to the health of your skin.
What causes the skin to change over time?
The foremost cause is inflammation.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is defined as the natural response of a healthy immune system to restrain pathogens and free radicals from entering the body. Did you know it can alter your DNA? Inflammation is a necessary measure in repairing the body. However, continuous inflammation leads to premature aging, acne, and chronic diseases like cancer, and autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and strokes, ultimately altering your DNA. It is no wonder that inflammation is called the silent killer.
What are the causes of inflammation?
Immune system malfunction– the immune system sometimes targets its response to the normal healthy cells seen in the case of psoriasis, asthma, Alzheimer’s, arthritis, etc.
Allergic reaction – when the body senses anything alien, it triggers a reaction, sometimes an overreaction. This leads to inflammation.
Certain foods, medications, and allergens like poison ivy, perfumes, and cosmetics also cause inflammation.
Environmental stress – Polluted air, and UV rays of the sun create free radicals inside the body that damage the skin and inside the body, sometimes irreversibly. It shows on the skin as melanoma, age spots, and loss of elasticity. According to the AAD (American Dermatology Association), 1 million Americans suffer from melanoma. It is the 2nd most common cancer in women between the ages of 15-29, and the 5th most common overall.
Toxic stress – Alcohol, tobacco, certain foods, and to a great extent, cosmetic products are some of the toxins we take inside the body, knowingly and unknowingly. These have a damaging effect on the lungs, liver, colon, and skin. Long-term use and exposure to these toxic substances result in inflammation within the cells, which leads to complications like diabetes.
Emotional stress – Life poses challenges and our way of responding to them determines our health. Accept things as they are, and you will be stress-free. Taking it to heart, you subject your body to enormous stress leading to inflammation. Continuous stress weakens the immune system. This, in turn, leads to inflammatory responses like fatigue, depression, etc. Cortisol is the hormone secreted by the body during extreme situations. Beware, a high level of cortisol in your body for an extended period is toxic and damaging to the immune system. It also causes irreversible damage at the DNA level. It leads to premature aging and other complications. According to consumers, aging skin is the second most concern in women ranking at 44%, next to acne.
Free radicals are known to be the key cause of inflammation. These free radicals are unstable molecules in our body that cause damage to our tissue and organs. It is an activated molecule released by the body due to sun, stress, and inflammatory ingredients such as highly processed foods. They are ‘free’ because they are missing a critical molecule, which allows them to pair with another molecule. So, they cause long chain chemical reactions in the body as they react with other molecules. It is called oxidation which causes premature aging and damage at the DNA level.
Lack of sleep is a common cause of inflammation in the body. It is through sleeping that the body heals itself to operate at its peak. Loss of sleep leads to the body being unable to recuperate. Continuous sleep deprivation leads to chronic inflammation, the effects of which are damaging to the body.
What are the types of inflammation?
Acute, continuous, and sub-clinical. Let us look into the three types a little more in detail;
Acute inflammation – a cut, a scraped knee, a broken bone, or bacterial and viral infections, triggers acute inflammation. It is a quick and severe response by the body’s immune system. Pain, swelling, and redness are the physical signs seen in such a response.
Continuous inflammation – is also called chronic inflammation. The immune system responds to any injury or infection by releasing antibodies, and proteins, and increased blood flow to the damaged area. The response lasts for a few hours or a few days. But if this response lingers for a longer time, it damages the healthy cells, tissues, and organs. A longer response can damage DNA and cause internal scarring. It leads to cancer, stroke, diabetes, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions. (https://www.healthline.com/process). According to Dr. Robert H. Shmerling, medical editor of Understanding Inflammation from Harvard Health Publishing and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School), “from the body’s perspective, it’s under consistent attack, so the immune system keeps fighting indefinitely.”
Unlike acute inflammation where the responses are visible, signs of chronic inflammation are subtle. Fatigue, body pain, depression or anxiety, gastrointestinal complications (diarrhea or constipation), weight gain or loss, and persistent infections are a few signs.
Sub-clinical Inflammation – Usually, inflammation occurs with visible symptoms such as red rashes and swelling. But there is yet another type of inflammation occurring at the cellular level that we refer to as sub-clinical inflammation. These micro inflammatory spots cannot be seen with the naked eye and require a microscope to be detected. Here, the skin is inflamed internally, altering the DNA, and leading to premature aging.
How can we prevent inflammation?
” People think inflammation needs to be stomped out at all times, but it plays an essential role in healing and injury repair to keep your body safe and healthy. Some inflammation is good. Too much is often bad. The goal is to recognize when inflammation is simply doing its job, and when it can potentially cause problems”, says Dr. Shmerling.
Ayurveda, called the Science of life, recognizes the role of inflammation in causing disease. In fact, Ayurveda has always focused on preventing and minimizing inflammation. Ayurveda believes in the power of the immune system; a strong immune system is a key to good health. It says disease does not occur in the body suddenly. It develops over time caused by stress, poor diet, faulty lifestyle, and lack of proper physical exercise. It also believes in preventing the disease from taking root rather than treating it after. In Ayurveda, the physical body and the mind are treated in tandem, not separately. It recommends:
- A balanced lifestyle and diet combined with Yoga and Meditation.
- Eating only seasonal fruits and vegetables, eating moderately.
- A simple, sustainable daily routine in alignment with the circadian rhythms
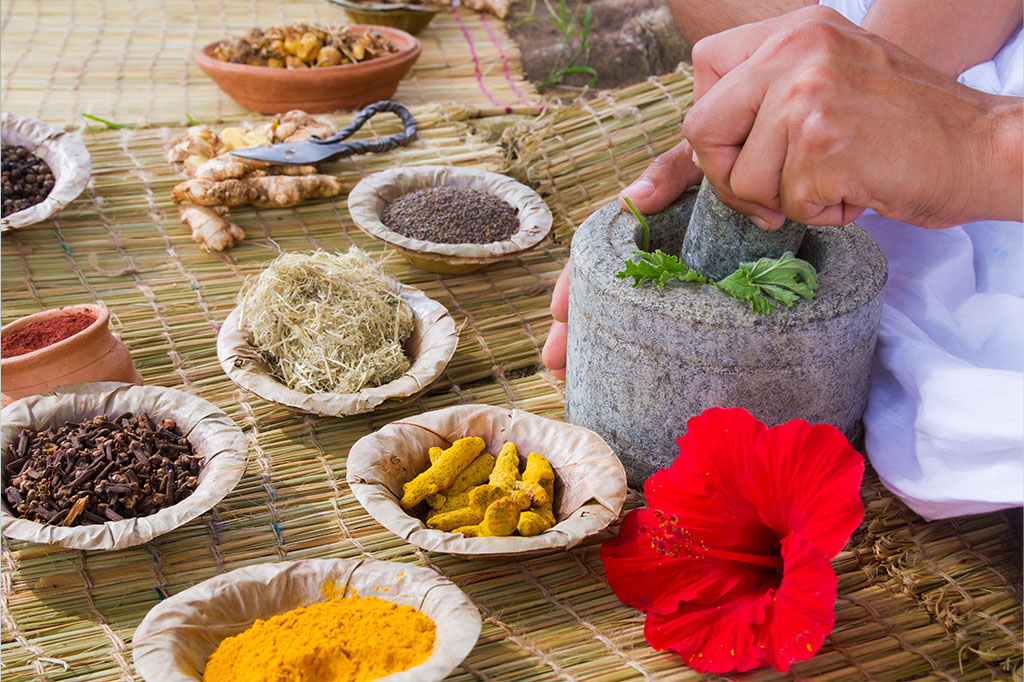



Turmeric, ginger, pepper, cloves, Amla (Gooseberry), and Gotu Kola are but a few of the thousands of spices and herbs that have been used in Ayurveda for millennia in treating inflammation.
Yoga is an ancient Indian practice that brings together the mind and body. It incorporates breathing exercises and meditation to help relax and reduce stress. It also promotes the release of endorphins, the feel-good hormones that affect how stress is handled. Breathing exercises, known as Pranayama in Sanskrit, teach you to relax, regulate your breath, and breathe deeply. It helps reduce stress and calm your body and mind.
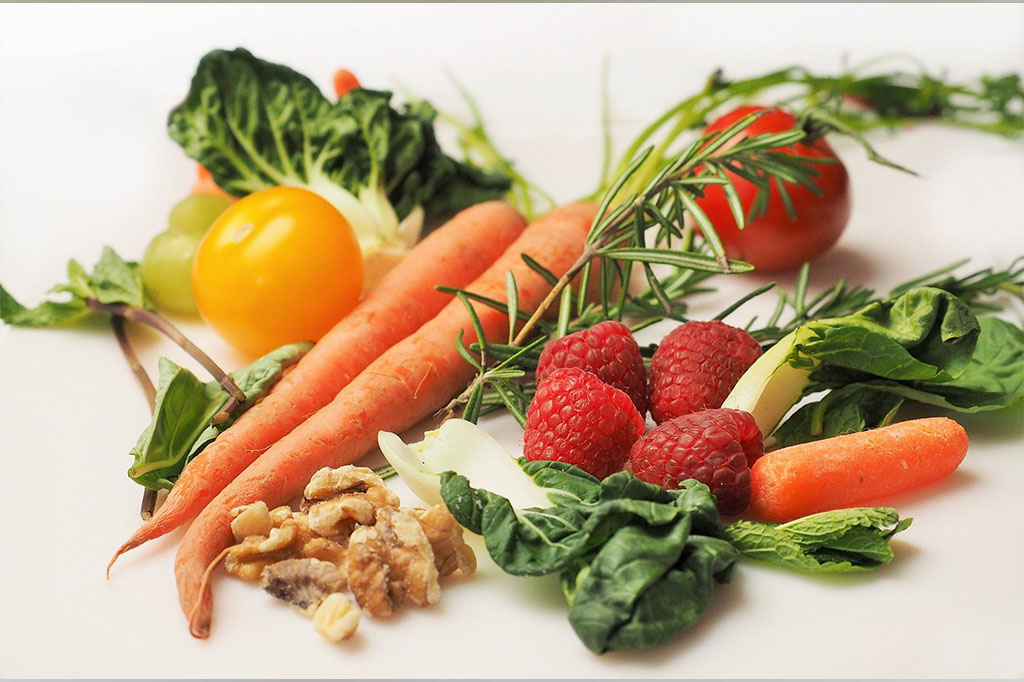
Diet plays an important role in preventing or minimizing inflammation. As Ayurveda says, food should be your medicine. In fact, the basic premise of Ayurveda is that if you eat right, there is no need for medicine, as the food itself is medicine. Foods that are nutritionally dense, and antioxidant-rich, especially polyphenols, are proven to reduce inflammation. It includes berries, cherries, plums, red grapes, onions, turmeric, green tea, olive oil, nuts and seeds, and dark green leafy vegetables like spinach and kale. It is recommended to eat all the colors of the rainbow on a daily diet. Colorful foods are rich in antioxidants. They help fight the free radicals that cause oxidative stress due to inflammation which in turn leads to premature aging.
Avoid foods high in simple sugars like soda, fruit juices with added sugars, sports drinks, processed meat, and refined carbs like white bread and pasta that cause inflammation. These foods are linked to problems related to chronic inflammation, such as heart disease, weight gain, and cancer.
In Conclusion
“It goes back to the basics: maintaining a healthy weight, choosing a good diet, getting plenty of sleep, and exercising regularly,” says Dr. Shmerling. The best approach is to prevent conditions related to inflammation even before it begins. Ayurveda really embodies this dictum, “Prevention is better than cure.”